Osteoarthritis Pain: Symptoms, Causes & Treatment Relief Options
Osteoarthritis is the most frequently occurring form of arthritis, affecting millions of individuals across the globe.
It is often termed as the wear-and-tear arthritis, and it takes place when the protective cartilage wears down at the ends of the bones.
While the condition may affect any joint of the body, it typically damages the joints in the neck, hands, lower back, hips and knees.
The disorder may gradually exacerbate with time and there is no cure found until today. Treatments are available to slow down its progression, improve joint function and relieve pain.
Signs and symptoms Of Arthritis

Symptoms often develop gradually and worsen with time. Some signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis typically include:
- Joint pain during or after movement
- Tenderness of the joint when you apply pressure to it
- Stiffness of the joint which will be most noticeable in the morning when you wake up or after a period of no activity
- Your joints may become less flexible and you will not be able to move them in their complete range of motion
- You may feel or hear a grating sensation while using the affected joint
- Bones spurs (hard lumps) may develop around the affect joint
When to seek medical help
See a doctor if stiffness and pain last for more than a few weeks.
Causes
Osteoarthritis takes place when the cartilage that protects and cushions the bone ends in your joints weaken or deteriorate over time. Cartilage is a strong, slippery tissue that prevents frictions between the joints and bones. When a person has osteoarthritis, the slick exterior of the cartilage roughens and eventually wears down, causing one bone to rub against the other.

Risk factors
Risk factors of osteoarthritis may include:
- Sex. Women are often more susceptible than men – the reason is not known.
- Age: As a person ages, his risk increases.
- Deformities of the bones. People born with defective cartilage or malformed joints are more at risk.
- Joint injuries. People with injuries that occur from sports or accidents are more at risk.
- Obesity. When a person is obese or overweight, he carries more body weight, thus his joints are under more stress.
- Occupational injuries. Certain jobs involve repetitive stress on the joints.
- Diseases. People with diabetes, gout, underactive thyroid or Paget’s disease of bone are more at risk.
- Lifestyle choices. People with a sedentary lifestyle or a poor diet may put themselves at risk.
Treatment
Although there is no known cure for osteoarthritis, treatments are available to relieve symptoms and improve joint function. Some of them include:
- Medications. Acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may reduce inflammation and alleviate pain.
- Therapy. A combination approach of the following therapies may be beneficial:
- Physical therapy. A physical therapist will guide you and create an exercise regimen to strengthen the muscles around the affected joint and improve its range of motion.
- Occupational therapy. An occupational therapist will help you find ways to perform everyday tasks and your job, while preventing excessive stress on the joint. For example, using a toothbrush with a large grip may make the job easier for those with finger osteoarthritis.
- Heat and cold therapy. Applying heat and cold packs can be beneficial. Cold packs relieve pain and muscle spasms, whereas heat relieves stiffness.
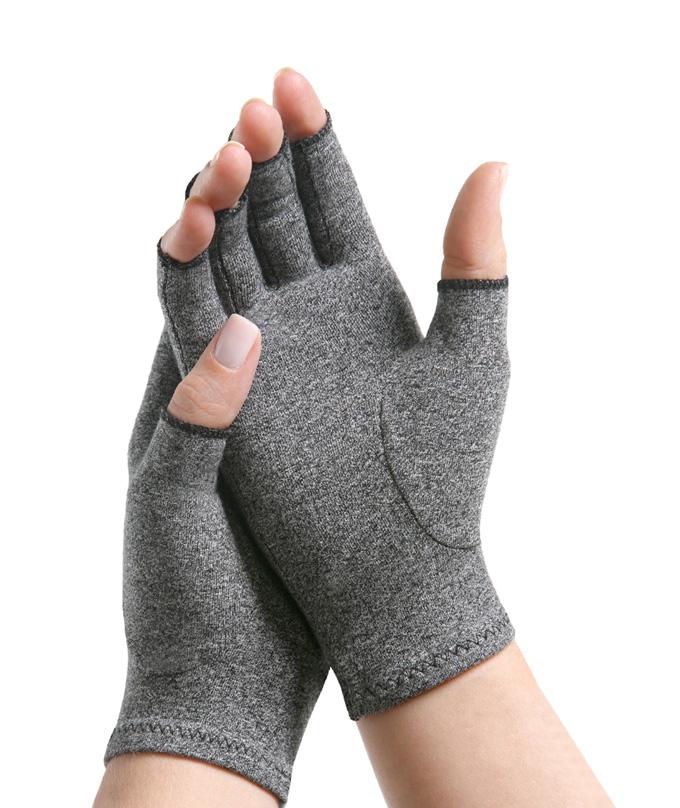
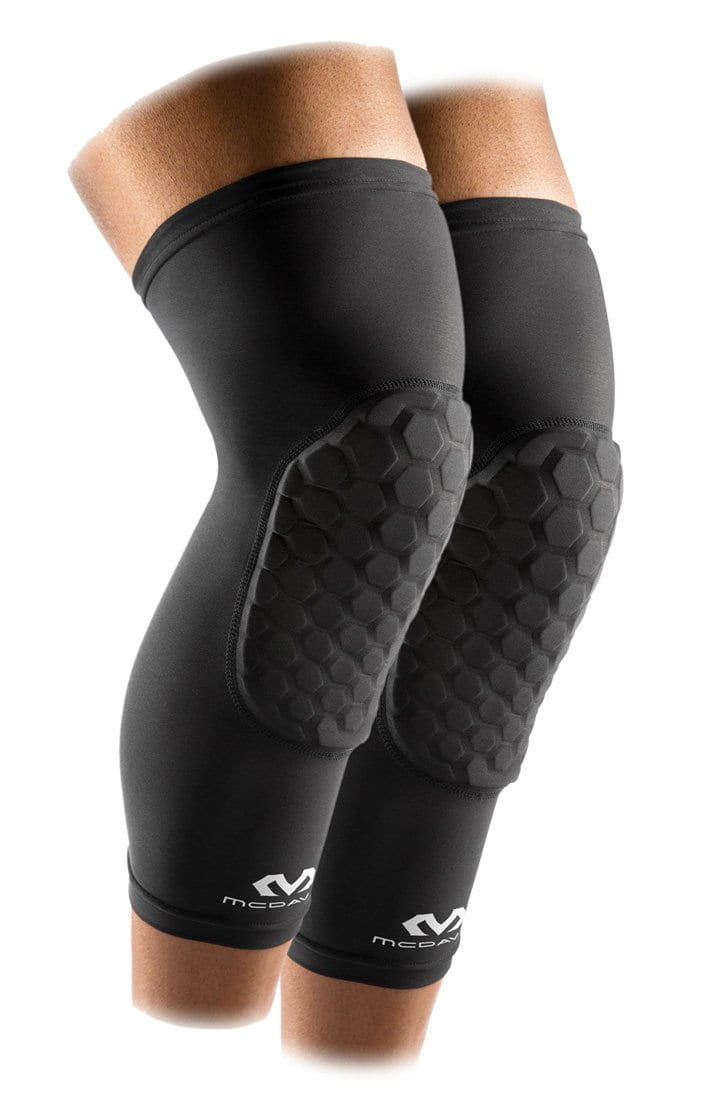
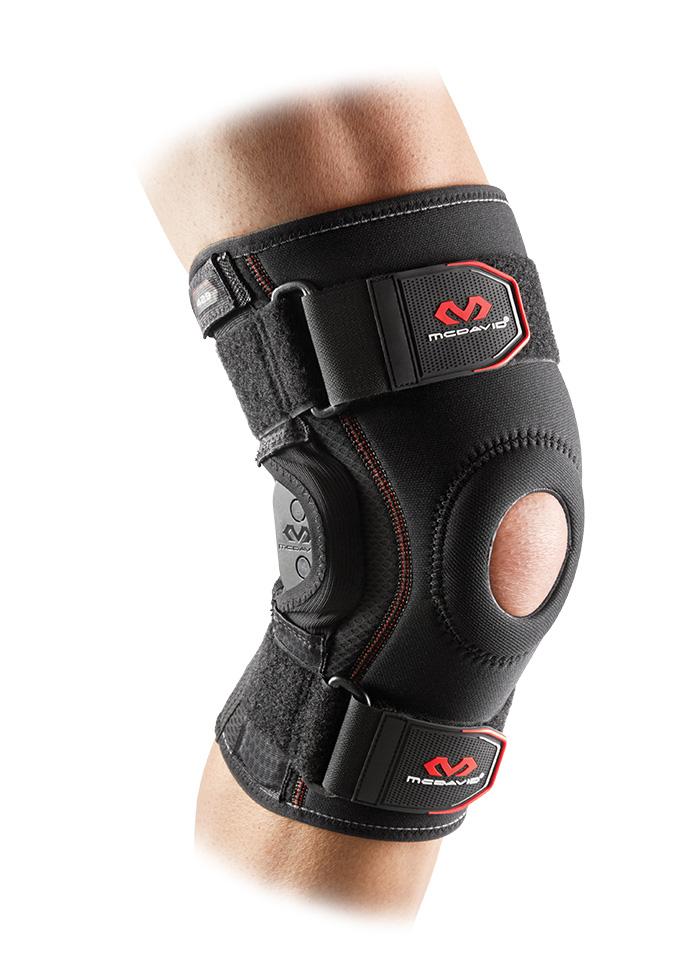
- Braces or shoe inserts. Splints, shoe inserts, braces and other medical devices may help relieve pain. The following are some extremely popular examples of wraps that support, immobilize and reduce stress and pressure on the affected joint:
- McDavid Arthritis Elbow Sleeve
- McDavid Arthritis Knee Sleeve
- IMAK Arthritis Gloves A2017
- IMAK Arthritis Socks A2019
Related Article: What Is Sacroiliitis & Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction? Causes, Symptoms & Treatment Options





Leave a comment