What Is Peroneal Tenonditis? Causes, Symptoms & Treatment Options
A tendon is a thick fibrous band of tissue that connects a muscle to a bone. There are two tendons or peroneal tendons that run side by side in your foot, behind the outer ankle bone. These tendons are called peroneus brevis and peroneus longus.
While one peroneal tendon attributes to the outer part of your midfoot, the other runs under your foot and attaches in close proximity to the inside of your arch. Your peroneal tendons are really important – they stabilize the ankle and foot and ensure your foot is safe from sprains and injuries.
One type of a peroneal tendon injury is peroneal tendonitis, which is the irritation and inflammation of one or both peroneal tendons. Peroneal tendonitis usually occurs because these tendons experience excessive strain, especially from activities involving a lot of standing and walking. In addition, certain types of feet may increase the force the tendons are subjected to, increasing a person’s risk of peroneal tendonitis.
Treatment is recommended to decrease symptoms and correct any defects that may play a role in the condition. Conventional treatments include anti-inflammatory medications, applying ice, activity medication and muscle strengthening, using ankle bracing and specific shoe inserts or orthotics. In rare cases, surgery may be needed.
Symptoms Of Personal Tendonitis
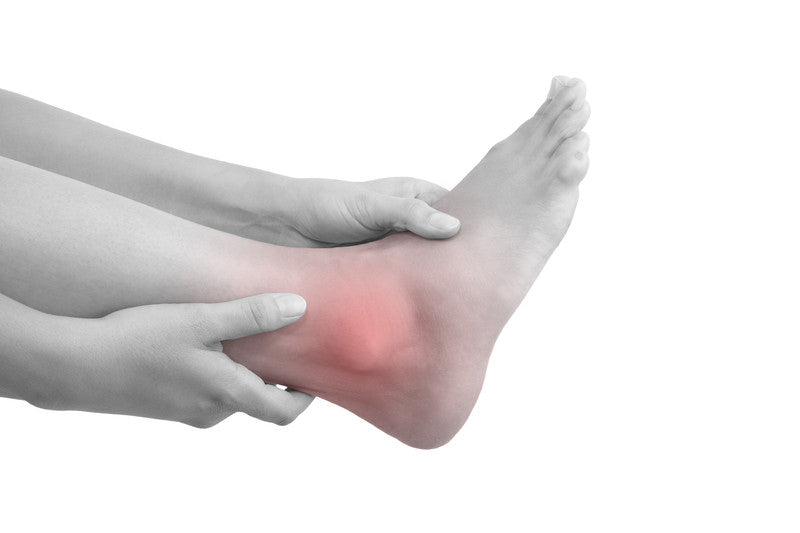
Peroneal tendonitis often causes pain on the outside of the ankle, right below the bony part of it. Pain worsens with activity and subsides with rest. You may feel pain while pressing on your peroneal tendons and this region may be warm to touch.
Causes
Some peroneal tendon injuries are acute, which means they occur suddenly and others are chronic, which develop over time.
Both types occur in people who participate in sports activities that involve repetitive movements of the ankle. Overuse causes the peroneal tendon to rub against the ankle bone, which leads to inflammation. This is common among runners as they run along slopes and experience excessive rolling out of the foot, making them prone to the injury. When the foot rolls outward, your peroneal tendon gets stretched more across the bone, boosting the friction between the two.
In addition, tight calf muscles increase peroneal tendon tension, allowing the tendon to rub against the bone more. This is the same case with overpronation of the foot due to higher arches or misaligned heels that are tilted inwards or inclined as they cause the tendon to rub against the ankle bone more as well, resulting in inflammation.
Treatment For Personal Tendonitis
Treatment measures often depend on the severity of the injury. Some options recommended by doctors include:
- Medications. OTC anti-inflammatory drugs may help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Physical therapy. Ice, heat or ultrasound therapy may help reduce swelling and pain. As symptoms improve, the physical therapist may teach you some exercises to help strengthen muscles and improve range of motion.
- Immobilization. A cast or splint may be needed to keep the foot and ankle in place and allow the injury to heal without worsening.
- Bracing. Your doctor may recommend using a brace for a short period to limit repetitive ankle movement during activities. An example is the McDavid Ankle Brace With Straps 195 which helps protect the ankle during an injury with great comfort, fit, and stability.
- Surgery. In some cases, surgery may be an option as the tendon or tendons may have to be repaired surgically. The most appropriate procedure will be chosen by the foot and ankle surgeon, depending on the patient’s lifestyle and condition. Following surgery, physical therapy is needed to rehabilitate the injured area.
You can check out another article: What Is Plantar Fasciitis? Causes, Symptoms & Treatment Options
Image Use:
You are allowed to re-use the image with the BodyHeal.com.au logo on your website or any online publication as long as the proper creditation is given to BodyHeal. You can link back to our homepage, or this article at






Leave a comment